Adapt better to physical, mental, And emotional stress
Where some medications are only able to boost or decrease a desired effect, evidence suggests that adaptogens have a unique ability to create balance based on a person's individual needs. One person may require more of something, while another requires less. For example, the same adaptogen that gives someone more energy can help to calm another person.*
Balancing stress hormones*
Stress is a chain reaction that results when the hypothalamus stimulates the pituitary gland to release the hormones that in turn cause the adrenal glands to release cortisol. Adaptogens are believed to help balance cortisol levels in the body by modulating the activity of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis. The exact mechanisms are not fully understood, but it is thought that adaptogens help balance cortisol levels when they are either too low or too high.*
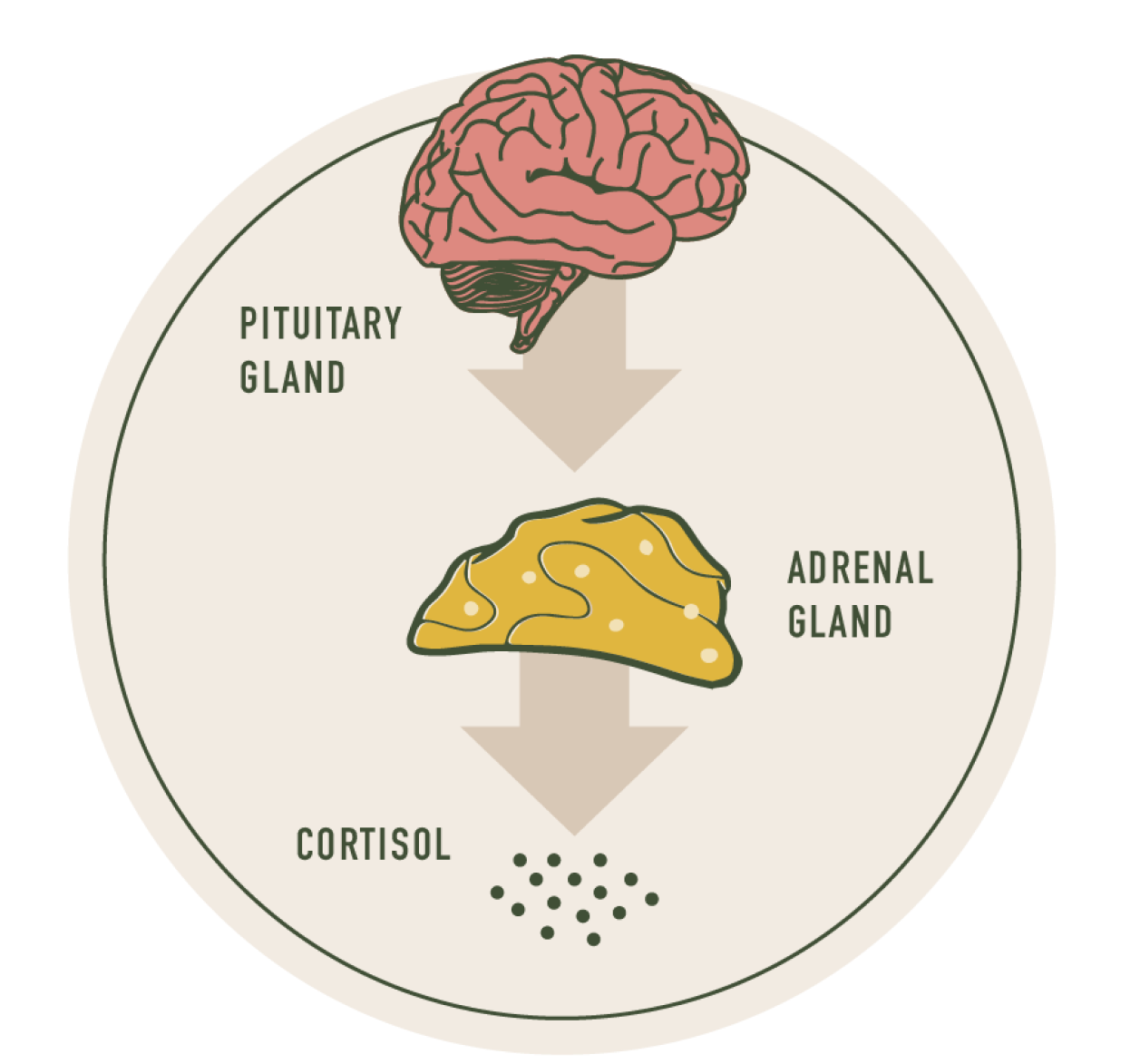
Balancing stress hormones*
High Cortisol Levels
Adaptogens can influence the HPA axis to help reduce excessive cortisol production and release. By regulating the stress response, adaptogens may help bring cortisol levels back to a more balanced range. High cortisol levels can cause weight gain, high blood pressure, osteoporosis, muscle weakness, and mood swings.*
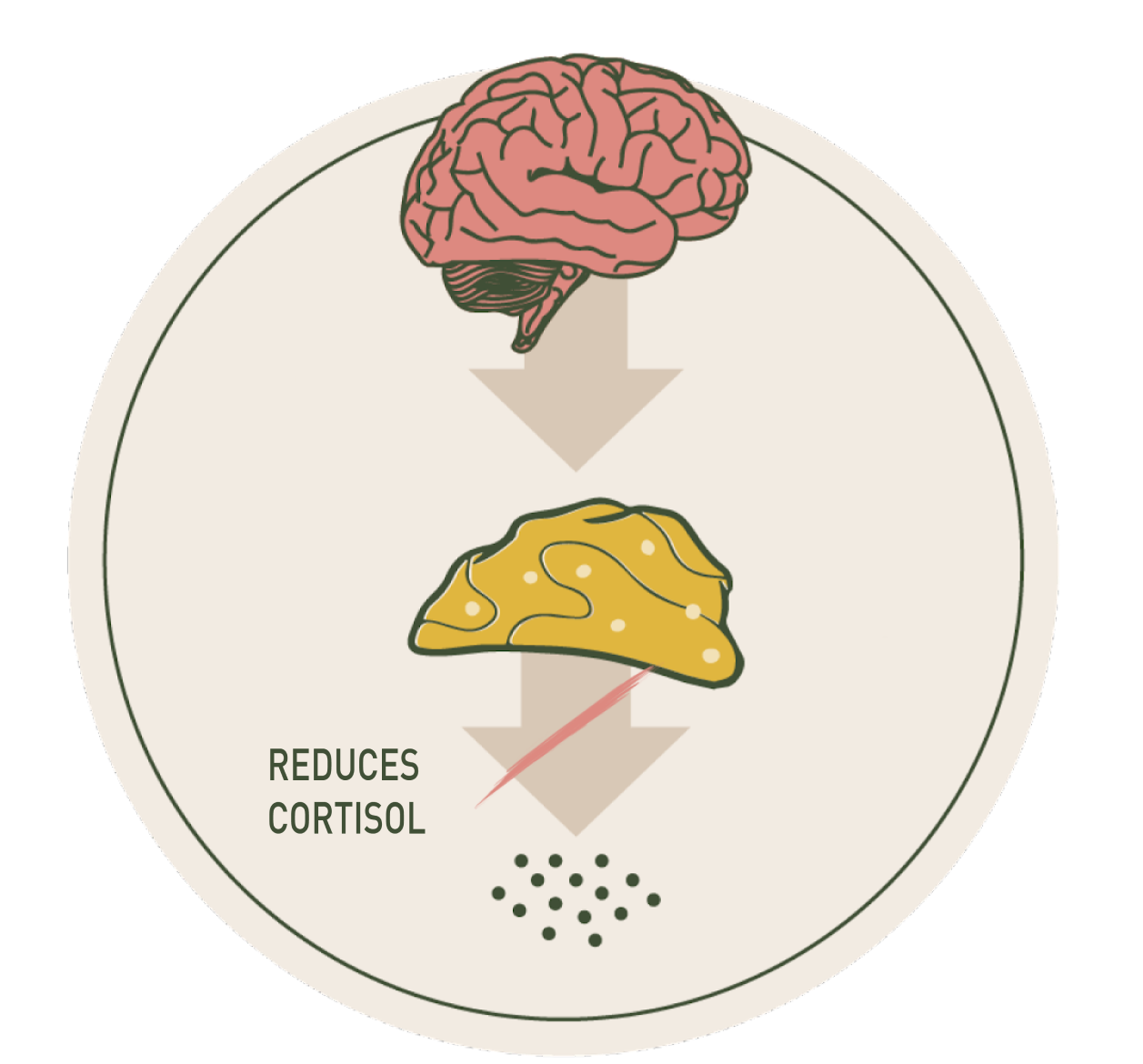
Balancing stress hormones*
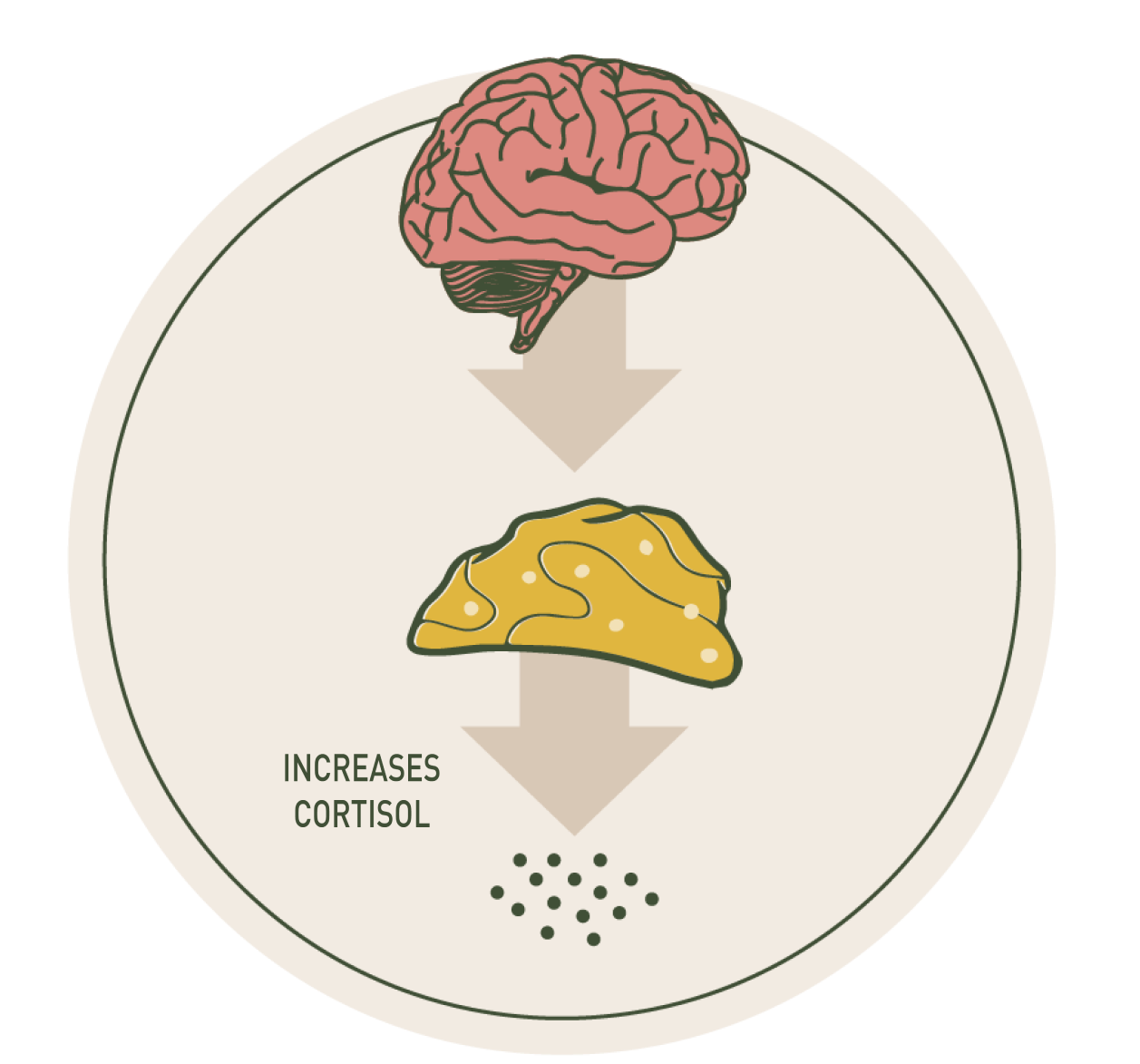
Low Cortisol Levels
Adaptogens can also stimulate the production and release of cortisol to bring it back to an optimal level. This can be particularly helpful for individuals experiencing adrenal fatigue or low cortisol due to chronic stress or other factors. Low cortisol levels can cause fatigue, depression, anxiety weakened immune system, and brain fog.*

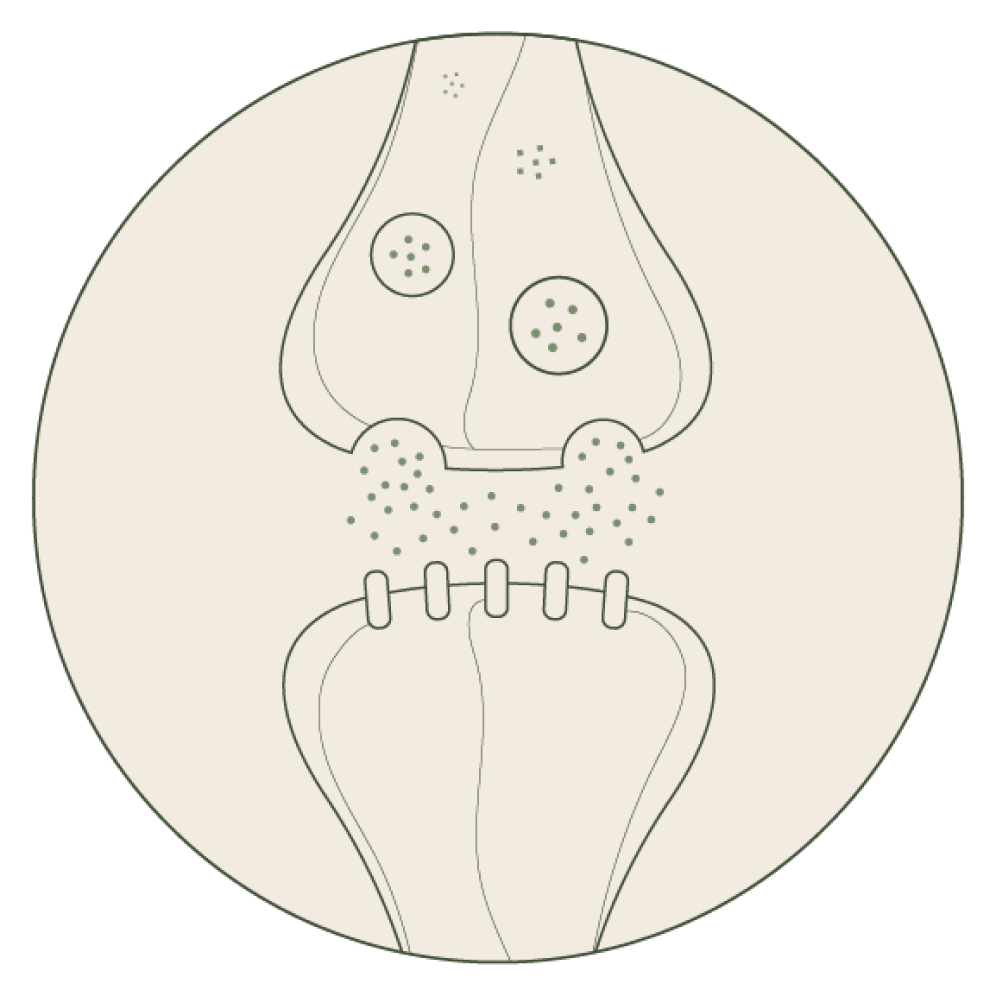
Stabilizing Brain Chemistry*
Adaptogens are thought to interact with neurotransmitter systems in the brain, particularly those involving serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine
SEROTONIN
Serotonin is often referred to as the "feel-good" neurotransmitter due to its role in regulating mood, anxiety, and sleep. Low levels of serotonin have been associated with conditions such as depression and anxiety disorders.*
SEROTONIN

Adaptogens may help regulate serotonin levels by influencing its production, reuptake, or breakdown. By modulating serotonin, adaptogens may contribute to a more balanced mood and improved emotional well-being.*
dopamine
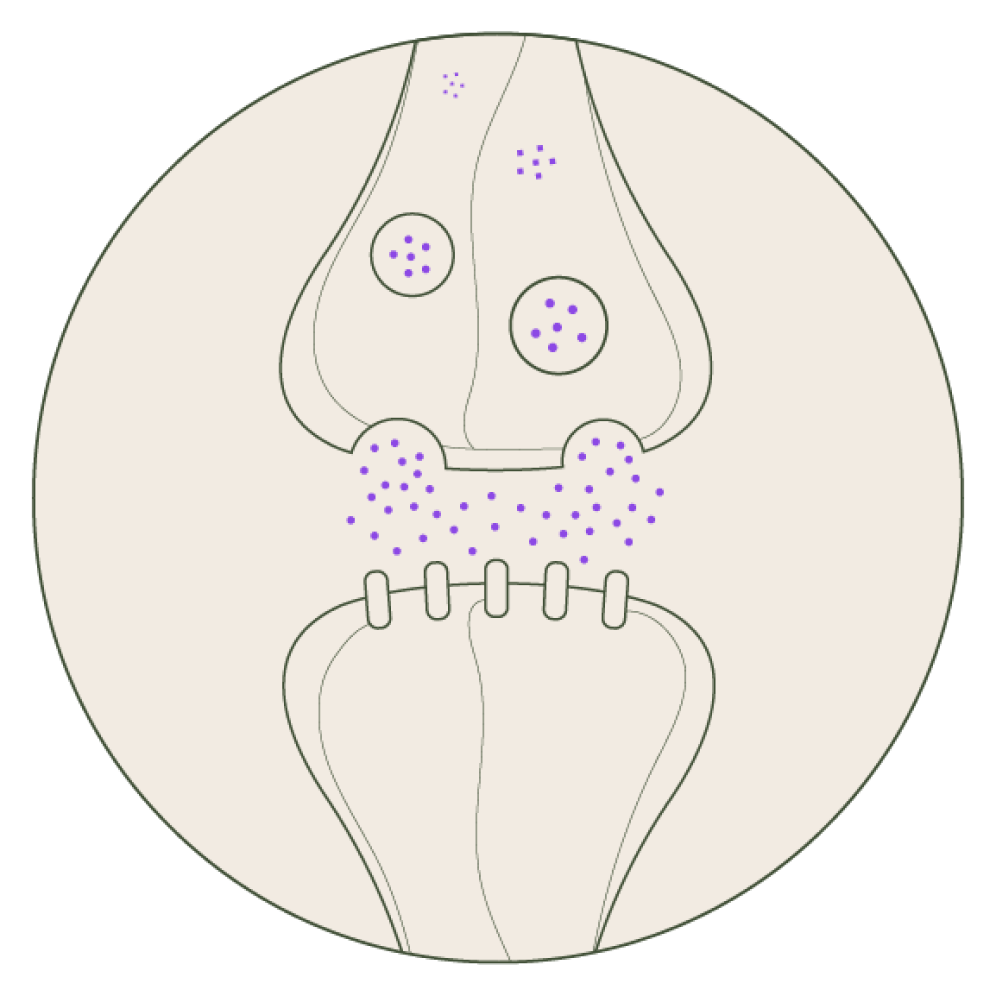
Dopamine is involved in reward, motivation, focus, and pleasure. Imbalances in dopamine levels have been linked to conditions such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), addiction, and mood disorders.*
dopamine

Adaptogens may affect dopamine by influencing its synthesis, release, or receptor sensitivity. By modulating dopamine levels, adaptogens may help enhance motivation, concentration, and overall cognitive function.*
norepinephrine
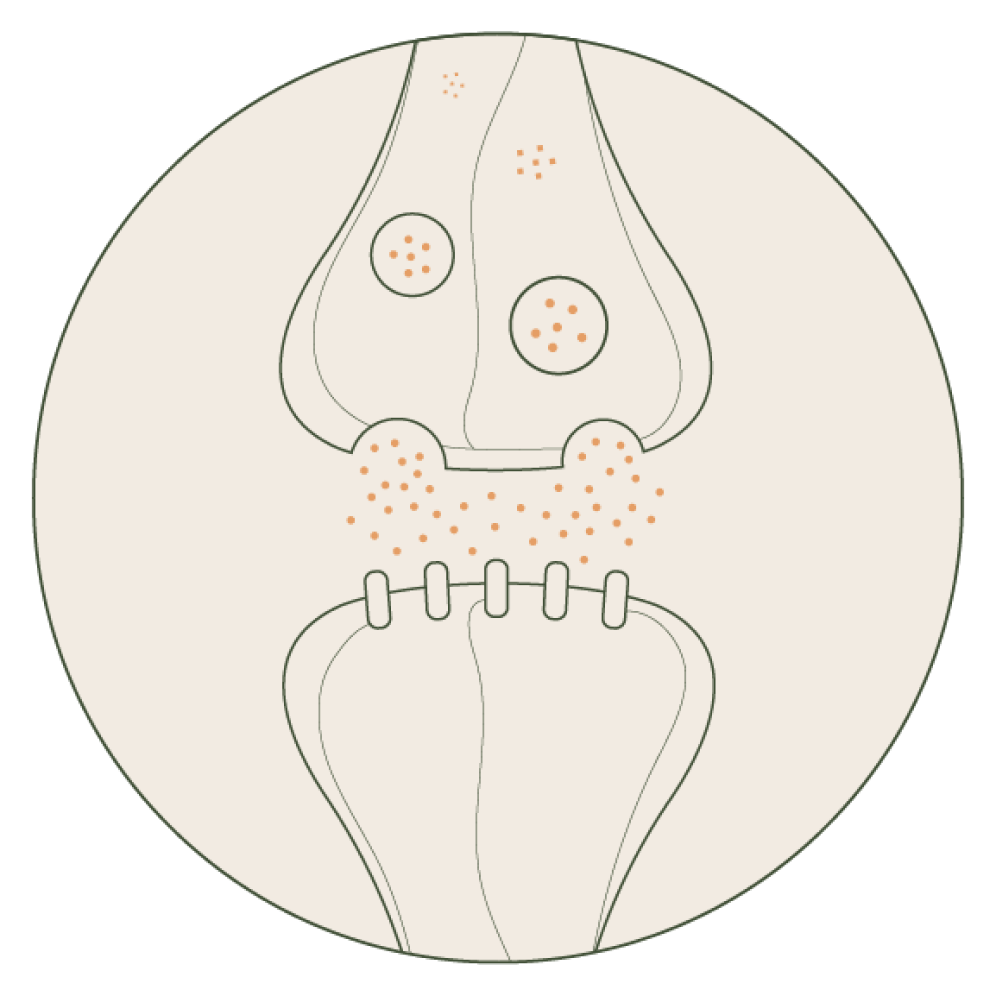
Norepinephrine, also known as noradrenaline, plays a role in alertness, attention, and stress response. Dysregulation of norepinephrine has been associated with conditions such as anxiety and attention disorders.*
norepinephrine

Adaptogens may impact norepinephrine levels by influencing its release or receptor activity. By modulating norepinephrine, adaptogens may contribute to improved focus, mental clarity, and stress resilience.*
Immune System Modulation
Adaptogens are thought to exert an immunomodulatory effect, helping to regulate and balance the immune response. They may assist in promoting a more appropriate immune response when it is underactive or dampening an excessive response when it is overactive. This regulation aims to support immune system balance and optimal function.*
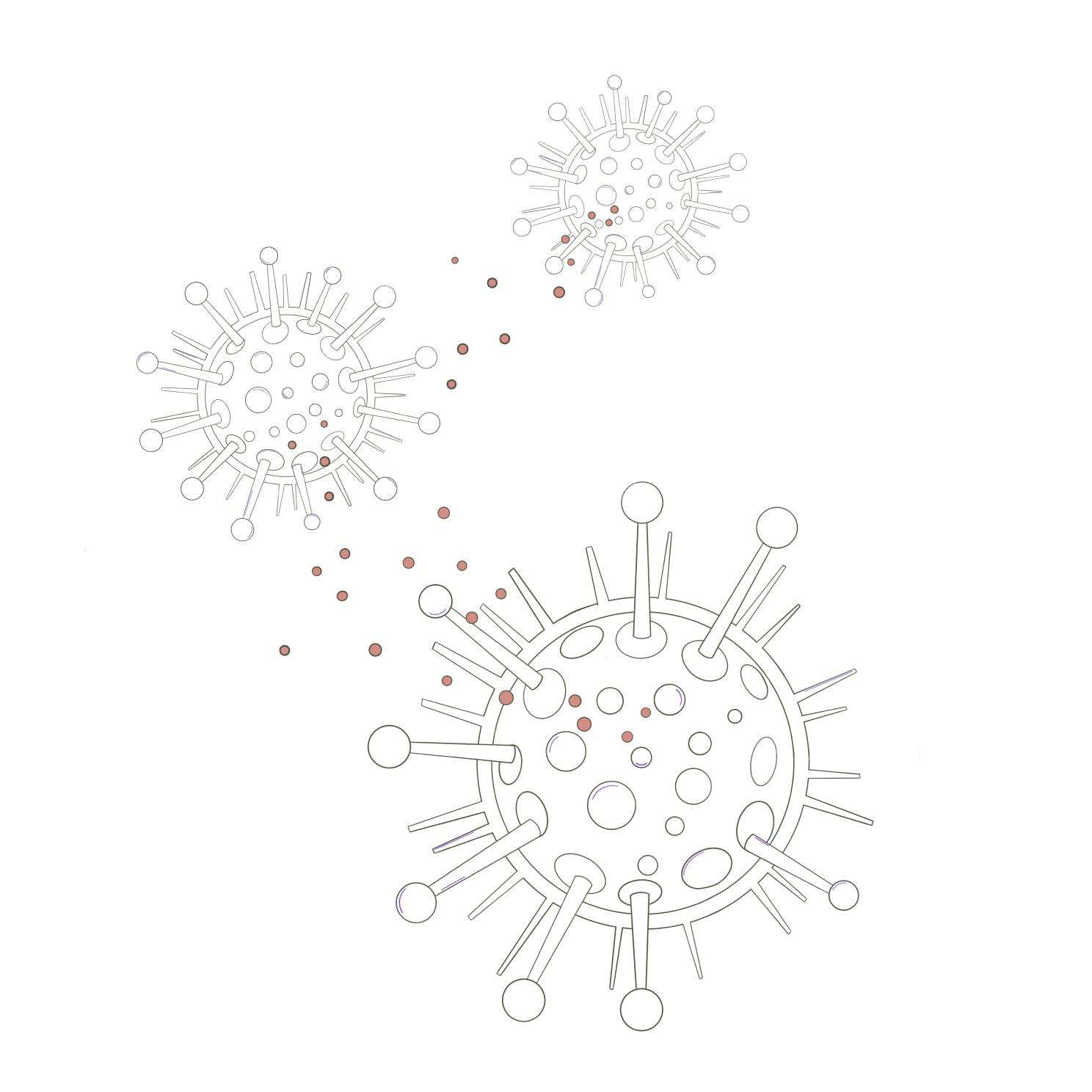
Immune System Modulation
Underactive Immune System
When the immune response is underactive, adaptogens may help promote a more appropriate and robust immune response. They can support the activation of immune cells, such as macrophages, natural killer cells, and T cells, which play crucial roles in detecting and eliminating pathogens. By enhancing immune cell activity, adaptogens may help strengthen the immune response and improve the body's defense against infections and diseases.*
Immune System Modulation
Overactive Immune System
When the immune response is overactive, such as in autoimmune conditions or allergies, adaptogens may help dampen the excessive immune reaction. They can exert modulating effects on immune cells and signaling molecules, such as cytokines, to help restore a balanced immune response. By reducing excessive immune activity, adaptogens may help alleviate symptoms associated with autoimmune disorders or allergic reactions.*
Antioxidant Activity
Many adaptogens possess antioxidant properties and can remove harmful free radicals that can cause oxidative stress. Antioxidants help remove these unstable molecules that can cause damage to cells and tissues, through a process called antioxidation.
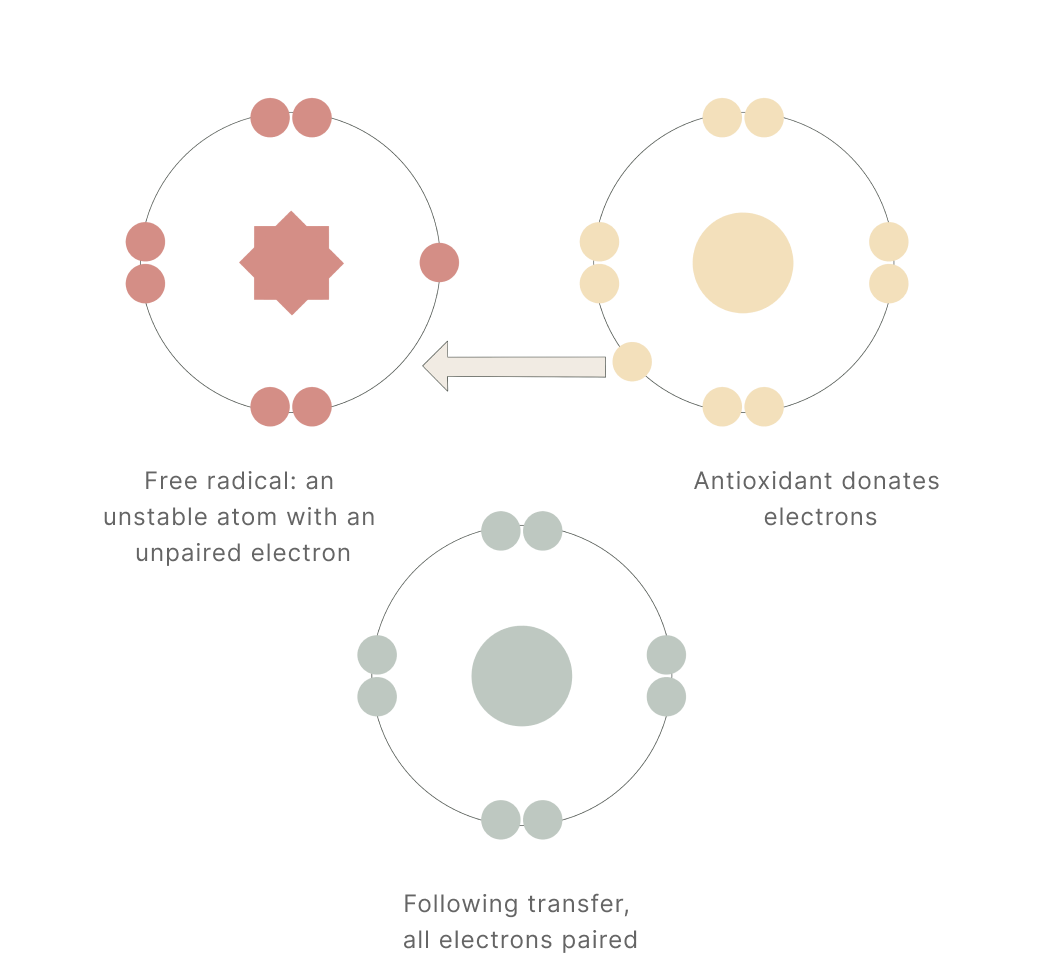
Antioxidant Activity
Antioxidants have the ability to donate electrons to free radicals. Free radicals are highly reactive molecules that contain unpaired electrons. Antioxidants, on the other hand, are stable molecules that can donate an electron to the free radical, effectively stabilizing it. By donating an electron, antioxidants help neutralize the reactivity of free radicals and prevent them from causing damage to other molecules.*


